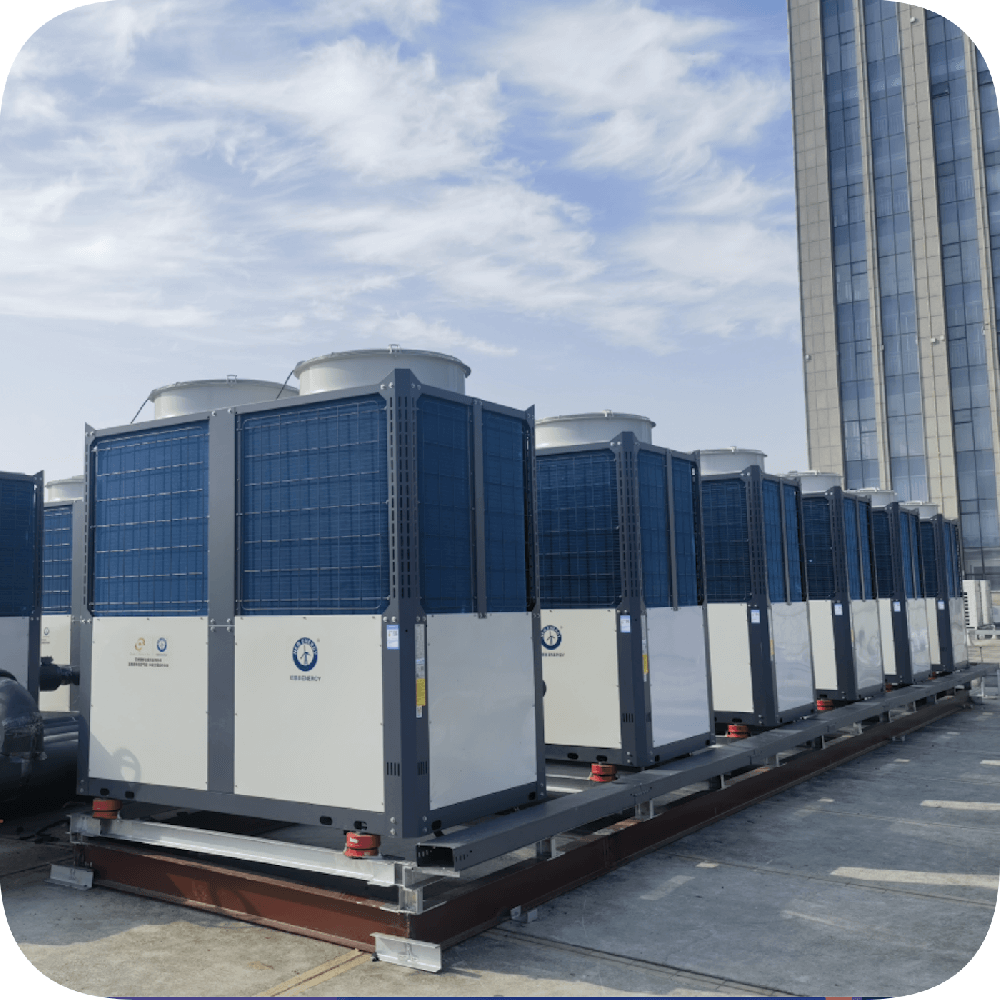
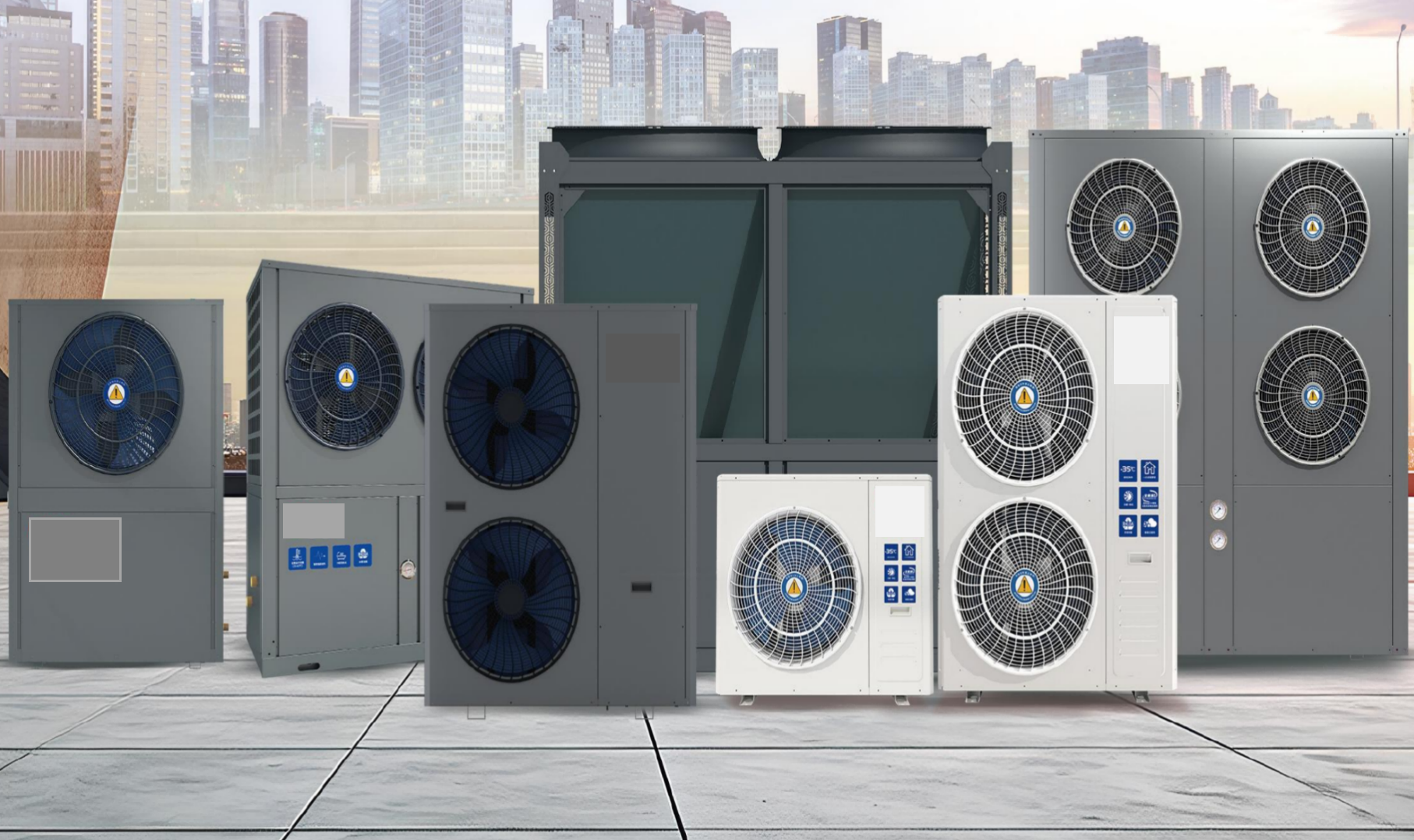
Heat Pump Water Heaters
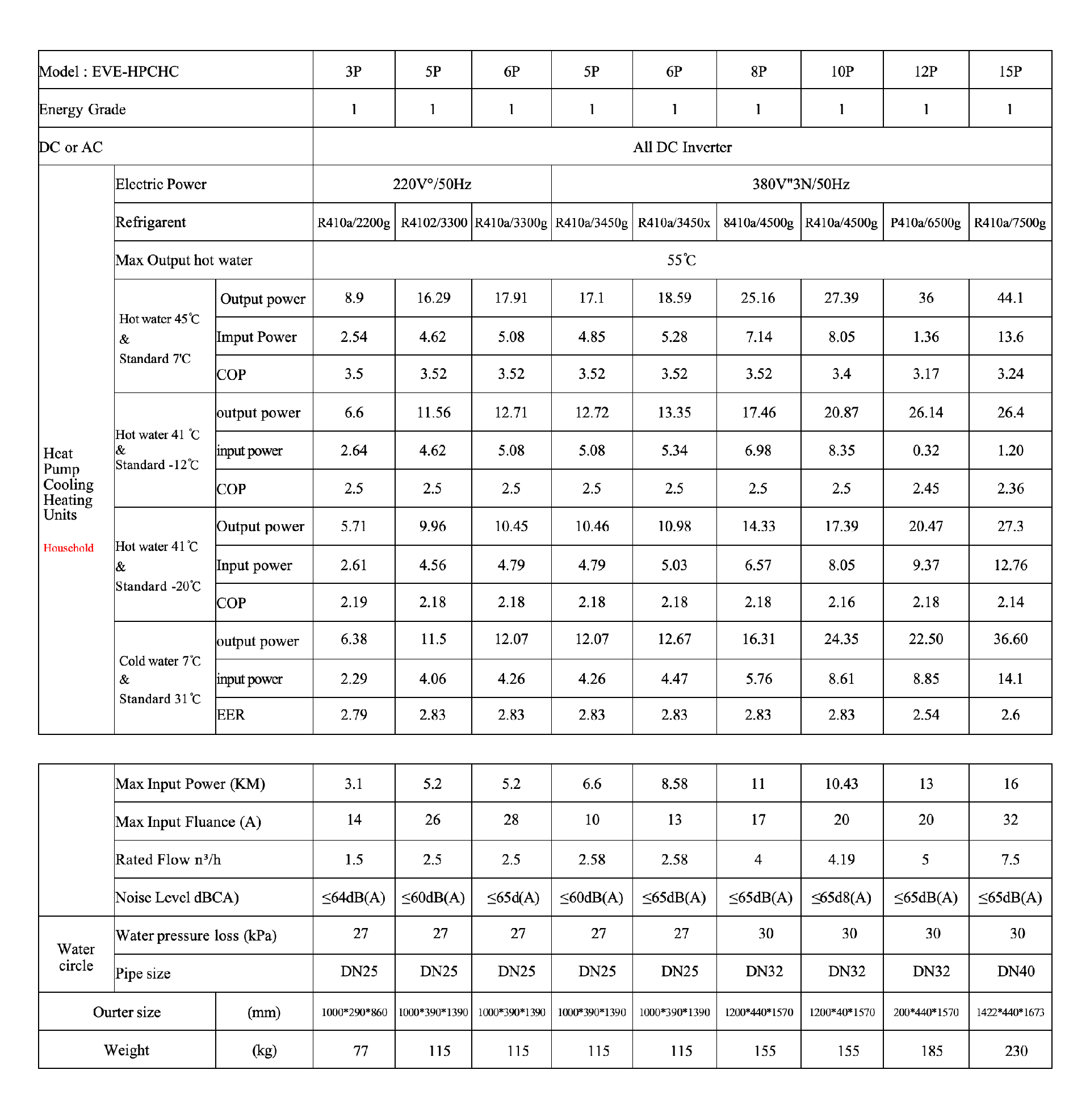
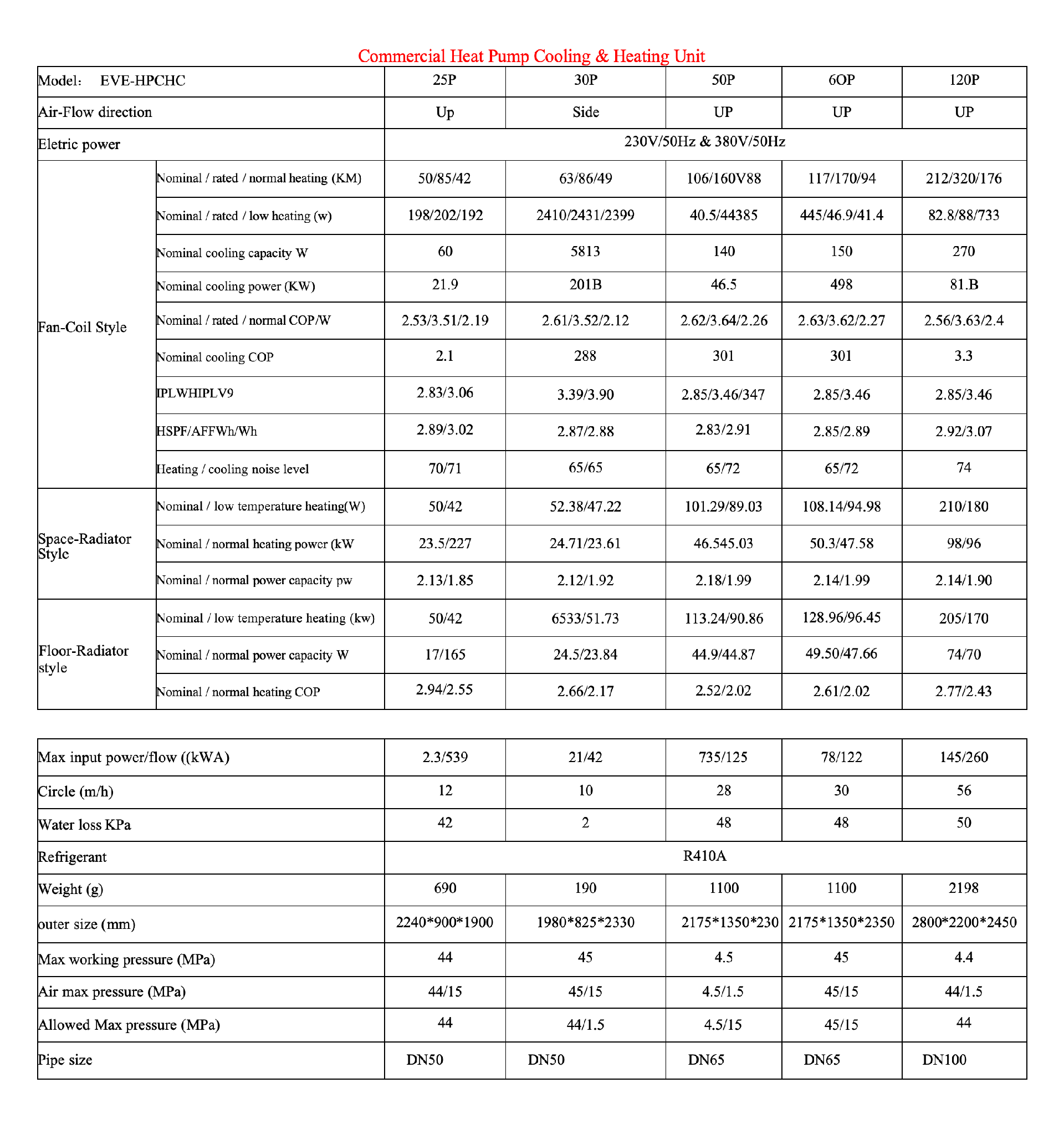
Heat Pump Cooling&heating Units
Heat Pump Cooling&Heating Units

Heat Pump Working Principle and Functions for Household and Commercial Use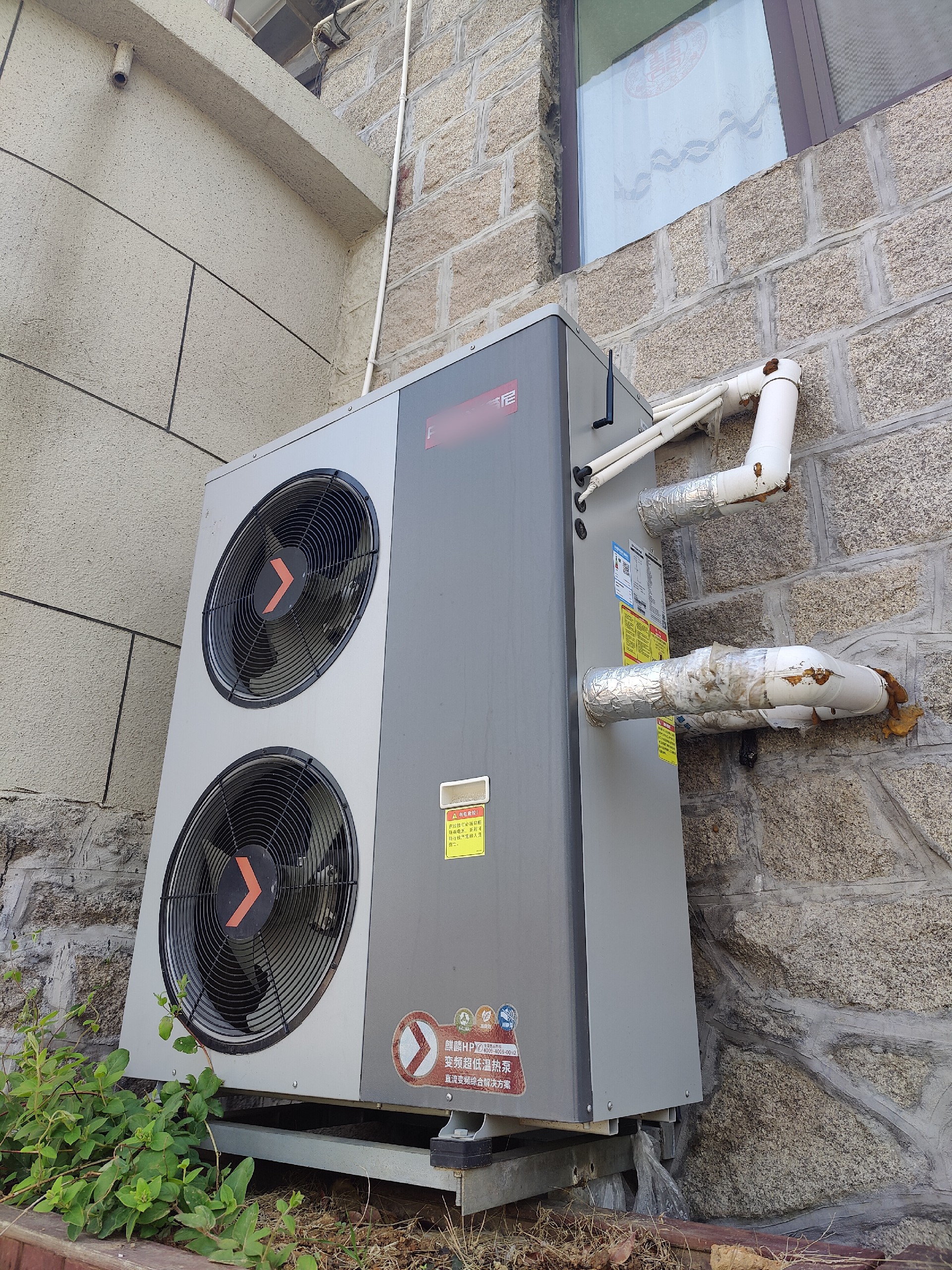
Working Principle:
Heat pumps transfer heat rather than generating it, leveraging the refrigeration cycle to move thermal energy between indoor and outdoor environments. Key components include a compressor, condenser, expansion valve, evaporator, and a reversing valve to switch between heating and cooling modes. The refrigerant undergoes phase changes (liquid ↔ gas) to absorb and release heat.
1. Heating Mode:
- Outdoor Unit (Evaporator): Absorbs heat from ambient air (even in cold temperatures) via the refrigerant, which evaporates into gas.
- Compressor: Increases gas pressure and temperature.
- Indoor Unit (Condenser): Hot gas releases heat indoors as it condenses back to liquid.
- Expansion Valve: Reduces refrigerant pressure, cooling it before restarting the cycle.
2. Cooling Mode:
- Reversing Valve redirects refrigerant flow.
- Indoor Unit (Evaporator): Absorbs heat from indoor air, cooling the space.
- Outdoor Unit (Condenser): Releases heat outside as refrigerant condenses.
Heat Sources:
| Air-Source | Most common, extracts heat from outdoor air. |
| Ground-Source (Geothermal) | Uses stable ground temperatures for higher efficiency. |
| Water-Source | Utilizes nearby water bodies. |
Functions & Benefits:
| Dual Functionality | Provides both heating and cooling with one system. |
| Energy Efficiency | Achieves COP 3–4, delivering 3–4 units of heat per unit of electricity. |
| Dehumidification | Removes excess moisture in cooling mode. |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces on-site fossil fuel use; pairs with renewables. |
| Versatility | Ducted or ductless (e.g., mini-splits) options suit diverse spaces. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Lower operating costs vs. traditional systems. |
Commercial Applications:
| Scalability | Larger systems or modular units for varied building sizes. |
| Zoning | Independent temperature control in different areas. |
| Variable-Speed Compressors | Enhances efficiency and comfort. |
Considerations:
- Cold Climates: Modern air-source models operate efficiently down to -15°C; supplemental heating may be needed in extreme cold.
- Upfront Costs: Higher initial investment (esp. geothermal), offset by long-term savings.
In summary, heat pumps offer efficient, flexible climate control for homes and businesses, reducing energy use and emissions while providing year-round comfort.

This kind of commercial heat pump hot water project unit is suitable to the colder north area to supply hot water for factory & hotel & hospital &swimming pool etc !!!
Heat pump water heaters are energy-efficient devices that provide hot water for both household and commercial use. They work by transferring heat from the surrounding air to the water, rather than generating heat directly. Here’s a detailed look at their functions and benefits:
Functions of Heat Pump Water Heaters:
1. Heat Transfer:
- Absorbing Heat: extract heat from the ambient air using a refrigerant system. This process is similar to how a refrigerator works but in reverse.
- Heat Exchange: The absorbed heat is transferred to the water stored in the tank, raising its temperature.
2. Energy Efficiency:
- Reduced Energy Consumption: By using ambient heat, consume significantly less electricity compared to traditional electric resistance water heaters.
- Cost Savings: Lower energy consumption translates to reduced utility bills, making cost-effective over time.
3. Hot Water Supply:
- Consistent Supply: provide a consistent supply of hot water, meeting the demands of both household and commercial settings.
- Storage Tank: Most come with an insulated storage tank to hold the heated water until it is needed.
4. Environmental Impact:
- Lower Carbon Footprint: Because they use less electricity, contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions, especially if the electricity comes from renewable sources.
- Eco-Friendly Refrigerants: Modern use environmentally friendly refrigerants that have a lower impact on the ozone layer.
5. Versatility:
- Multiple Modes: Many offer different operating modes, such as hybrid (combining heat pump and electric resistance), electric-only, and heat pump-only modes, allowing users to optimize performance based on their needs.
- Climate Adaptability: While are most efficient in warm climates, many models are designed to work effectively in a range of temperatures.
Benefits in Household and Commercial Services:
Household:
| Energy Savings | Homeowners can significantly reduce their energy bills by using. |
| Space Heating | In some setups, can also contribute to space heating, providing additional energy savings. |
| Quiet Operation | operate more quietly compared to traditional water heaters. |
Commercial:
| High Demand | Commercial establishments with high hot water demand, such as hotels, gyms, and restaurants, can benefit from the efficiency and cost savings. |
| Scalability | systems can be scaled to meet the large hot water needs of commercial buildings. |
| Sustainability | Businesses aiming for green certifications or sustainability goals can leverage to reduce their environmental impact. |
Installation and Maintenance:
1. Installation:
- Location: should be installed in locations with adequate airflow and space, such as basements or utility rooms.
- Professional Installation: Proper installation by a qualified technician ensures optimal performance and safety.
2. Maintenance:
- Regular Checks: Periodic maintenance, including checking the refrigerant levels and cleaning the air filters, ensures efficient operation.
- Longevity: Regular maintenance can extend the lifespan, providing reliable service for many years.
Summary:
Heat pump water heaters are an energy-efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly solution for providing hot water in both household and commercial settings. By leveraging ambient heat, they offer significant energy savings and contribute to lower utility bills and reduced carbon footprints. Their versatility and scalability make them suitable for a wide range of applications, from single-family homes to large commercial establishments.
Heat Pump Cooling&Heating Units
Advantages of Commercial Heat Pump Hot Water Systems

1. Energy Efficiency: Heat pumps are highly efficient, typically providing 3-4 units of heat for every unit of electricity consumed, making them more efficient than traditional electric or gas water heaters.
2. Cost Savings: Due to their high efficiency, heat pumps can significantly reduce energy bills, especially in regions with moderate to warm climates.
3. Environmental Benefits: Heat pumps produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuel-based systems, contributing to a lower carbon footprint.
4. Versatility: They can be used in various commercial settings, including hotels, hospitals, gyms, and laundries, where large amounts of hot water are required.
5. Long Lifespan: Heat pump systems generally have a longer lifespan compared to conventional water heaters, often exceeding 15 years with proper maintenance.
6. Rebates and Incentives: Many governments and utilities offer rebates and incentives for installing energy-efficient heat pump systems, reducing the initial investment cost.
Designing a Commercial Heat Pump Hot Water System
1. Assess Hot Water Demand:
- Determine the peak hot water demand (e.g., gallons per hour or liters per hour).
- Consider the temperature requirements for different applications (e.g., 120°F for domestic use, 140°F for commercial kitchens).
2. Select the Right Heat Pump:
- Choose a heat pump with the appropriate capacity to meet the peak demand.
- Consider the Coefficient of Performance (COP) and the Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) to ensure energy efficiency.
- Decide between air-source, water-source, or ground-source heat pumps based on the availability of resources and site conditions.
3. System Configuration:
- Standalone System: A single heat pump unit serving the entire hot water demand.
- Centralized System: Multiple heat pumps connected to a central storage tank, suitable for large facilities.
- Decentralized System: Smaller heat pump units installed at various points of use, ideal for buildings with dispersed hot water needs.
4. Storage Tank:
- Size the storage tank to handle peak demand and provide a buffer during low usage periods.
- Insulate the tank to minimize heat loss.
5. Integration with Existing Systems:
- Integrate the heat pump system with existing boilers or solar water heaters for hybrid operation, ensuring redundancy and efficiency.
- Use smart controls to optimize the operation of the heat pump based on demand and energy prices.
6. Piping and Distribution:
- Design the piping network to minimize heat loss and ensure quick delivery of hot water.
- Use recirculation pumps to maintain hot water availability at all points of use.
7. Controls and Automation:
- Implement advanced control systems to monitor and optimize the performance of the heat pump.
- Use timers, thermostats, and demand-based controls to reduce energy consumption during off-peak hours.
8. Maintenance and Service:
- Plan for regular maintenance to ensure the system operates efficiently.
- Include easy access to components for servicing and repairs.
9. Compliance and Safety:
- Ensure the system complies with local building codes and regulations.
- Include safety features such as pressure relief valves and temperature controls.
10. Economic Analysis:
- Conduct a cost-benefit analysis to evaluate the return on investment (ROI).
- Consider the total cost of ownership, including installation, operation, and maintenance costs.
By carefully designing a commercial heat pump hot water system, businesses can achieve significant energy savings, reduce operational costs, and contribute to environmental sustainability.





